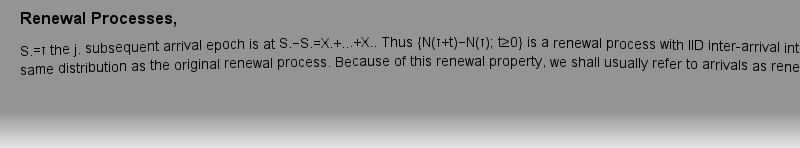作者: 不給啤 時(shí)間: 2025-3-25 18:50

作者: 狂熱文化 時(shí)間: 2025-3-25 21:38
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-81808-0g happens as an., and thus we refer to S.as the epoch of the n.arrival, or the n.arrival epoch. In principle, an arrival process can be characterized by a rule specifying the joint distribution functions of {S.,S.,…, S.} for all n≥1, but usually these distribution functions are derived in terms of other random variables.
作者: 紅潤(rùn) 時(shí)間: 2025-3-26 02:29
Introduction and Probability Review,arrivals to some system. The arrivals might be incoming jobs for a computer system, arriving packets for a communication system, patients in a health care system, or orders for some merchandising warehouse.
作者: 萬(wàn)靈丹 時(shí)間: 2025-3-26 05:13

作者: watertight, 時(shí)間: 2025-3-26 09:54
Textbook 1996 time scale), or are characterized by discreteoccurrences at arbitrary times. .Discrete Stochastic Processes.helps the reader develop the understanding and intuition necessary toapply stochastic process theory in engineering, science and operationsresearch. The book approaches the subject via many s
作者: Adrenal-Glands 時(shí)間: 2025-3-26 15:32

作者: 平淡而無(wú)味 時(shí)間: 2025-3-26 19:58

作者: 大猩猩 時(shí)間: 2025-3-26 21:47

作者: 影響帶來(lái) 時(shí)間: 2025-3-27 04:00
0893-3405 t satisfied. ..Audience:. An excellent textbook for a graduate level course inengineering and operations research. Also an invaluable reference forall those requiring a deeper understanding of the subject. .978-1-4613-5986-9978-1-4615-2329-1Series ISSN 0893-3405
作者: 我不明白 時(shí)間: 2025-3-27 06:52
Textbook 1996over formal rigor, and simplicityover generality. Numerous examples are given to show how results failto hold when all the conditions are not satisfied. ..Audience:. An excellent textbook for a graduate level course inengineering and operations research. Also an invaluable reference forall those requiring a deeper understanding of the subject. .
作者: atrophy 時(shí)間: 2025-3-27 12:04

作者: LEER 時(shí)間: 2025-3-27 13:56

作者: fabricate 時(shí)間: 2025-3-27 18:53

作者: DEFER 時(shí)間: 2025-3-27 22:01
9樓
作者: magnate 時(shí)間: 2025-3-28 05:53
9樓
作者: 急性 時(shí)間: 2025-3-28 08:51
10樓
作者: CHAFE 時(shí)間: 2025-3-28 11:35
10樓
作者: athlete’s-foot 時(shí)間: 2025-3-28 15:20
10樓
作者: 肉身 時(shí)間: 2025-3-28 20:26
10樓
| 歡迎光臨 派博傳思國(guó)際中心 (http://www.pjsxioz.cn/) | Powered by Discuz! X3.5 |